Introduction
In the earlier days, most cars had rear-wheel drive (RWD), and a differential system was used. But, as the car manufacturers invested in Research & Development, other types of drives were developed. The drives that came into prominence are front-wheel drive (FWD), all-wheel drive (AWD), and 4-wheel drive (4WD). Post 1970s and 1980s, FWD cars became popular due to their multiple advantages.
The cars available in the market today give you plenty of choices to choose from. When you are buying a car, there are many considerations like whether to buy a small car, a big car, an SUV, technological features, safety features, and type of drive.
One of the decisions you should make when buying a car is its drive or drive train system. The drive system of a car explains, where the engine power goes when you press the accelerator.
The engine power can go to the front wheels, rear wheels, or all four wheels. Depending on where the engine power goes, the drive system of a car can be FWD (front-wheel drive), RWD (rear-wheel drive), AWD (all-wheel drive), or 4WD (4-wheel drive). And your choice depends largely on how and where you want to drive the car.
This article tells you about the different drive systems and their pros and cons and makes you wiser on this subject. The sub-topics of this article are:
- What is a drive train
- Different types of drives in a car and their pros & cons
- Are AWD and 4WD drives are the same
- Why FWD cars are popular in India
- What is a differential and how it works
What is a drive train?
You can define a car’s drive train as a system that transmits the power from the engine to the wheels. A drive train moves the vehicle by transmitting the engine power to the wheels.
The drivetrain of your car consists of units that connect the car’s drive wheels to the transmission system. The major transmission units are the clutch, gear shift system, gearbox or transmission unit, propeller shaft, universal joints, differential, etc. A drive train delivers the power generated by the engine to the wheels.
You can also say that a drive train is a set of units in your car that works together to turn the car wheels. A power train includes a drive train and an internal combustion engine.
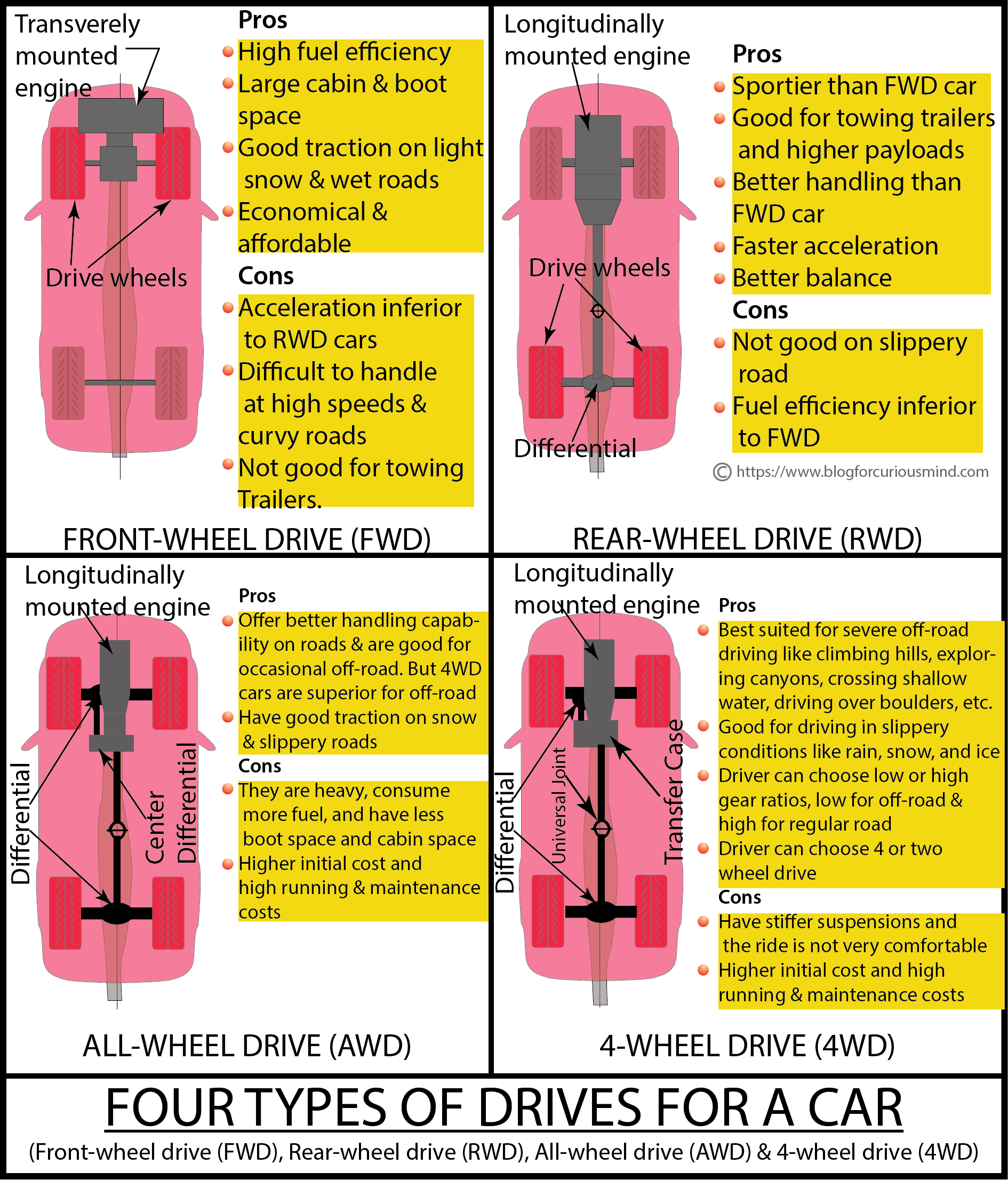
Different types of drives in a car and their Pros & Cons.
The different types of drives of a car are:
- Rear-wheel drive (RWD)
- Front-wheel drive (FWD)
- All-wheel drive (AWD)
- 4-wheel drive (4WD)
Rear-wheel drive (RWD)
In a Rear-wheel drive (RWD) car, the power from the engine drives the rear wheels. And the front wheels do not receive any drive. The front wheels concentrate on doing the steering job
The RWD drive system was started by Carl Benz in 1885. In this system, the power from the engine flows through the engine, clutch, and gearbox to a propeller shaft and the propeller shaft drives the rear wheels through a differential. The differential, mounted on the rear axle, distributes the power to the two rear wheels.
Until the 1970 RWD vehicles were the most common since there was no cost-effective way for the front wheels to steer and drive.
RWD cars normally have a longitudinally mounted engine at the front. The drive flows to the rear wheels through a transmission system including a propeller shaft and differential.
Rear-wheel drives are found on pickup trucks, sports cars, vans, SUVs, high-performance, and luxury cars. The uniform weight distribution of the RWD transmission makes them easy to handle. However, RWD cars are not best for slippery roads.
Pros of a RWD car
- RWD cars are sportier than FWD cars
- The driver can make the RWD car rear wheels slide out when cornering.
- RWD cars can handle higher horsepower and weight. This is the reason you find sports cars, police cars, and racing cars have RWD systems.
- RWD system is good for towing trailers and higher payloads. And this is the reason it is used in light and heavy pickup trucks/vans.
- An RWD car allows you to handle it better, especially when making a sharp turn at the corner. The reason is the front wheels have only a steering job. Not driving and steering as in an FWD.
- Handling an RWD car is easier than handling an FWD car, especially on winding roads and high speeds.
- An RWD car has faster acceleration compared to an FWD car of the same tire size and capacity.
- A RWD car has better balance since the weight of the power train is more evenly spread over the length.
- A RWD car can have its engine in the front, middle, or rear. But a FWD car engine must be in front.
- Maintenance cost is not very costly.
Cons of a RWD car
- The propeller shaft running under the chassis consumes space. The result is less boot space and passenger space.
- The power loss in an RWD car is more than a FWD car and affects fuel efficiency.
- The traction of an RWD car on a slippery road (ice, snow, rain, etc) is inferior compared to a FWD car.
Front-wheel drive (FWD)
In a front-wheel drive (FWD) car the power from the engine drives the front wheels. The rear wheels do not receive the drive. So, the front wheels of an FWD car drive the car and steer it.
An FWD car normally has its engine mounted transversely since it gives sufficient space for mounting the gearbox and drive system.
Automobile companies have been trying to develop an FWD car for a long. However, FWD cars were popularized during the 1970s and onwards. Today most of the cars available in the market have FWDs.
Pros of FWD car
- Front-wheel drive cars have high fuel efficiency. Because the engine and the drive train are nearest to the front wheels, and the power loss is minimal. The reduced number of transmission parts makes the car light and fuel-efficient.
- FWD cars emit less carbon dioxide.
- The engine and transmission mounted at the front of an FWD car impart good stability and traction on light snow and wet roads.
- FWD cars have larger boot space and passenger space. Because all the drive parts are in the front and no drive parts underneath. This is the reason why the majority of cars today have front-wheel drive systems.
- FWD cars have less transmission loss compared to RWD cars. Also, they have better fuel efficiency.
- The front-wheel drive system has a simple design, easy to manufacture, and the number of parts is comparatively less. This makes FWD cars economical and affordable.
- Fewer parts mean low maintenance cost
Cons of a FWD car
- The FWD car suffers from the issue of understeer since it has to drive and steer. And this can take out the fun of driving it, especially when turning the corners. Also, driving a FWD car at high speed is tough.
- Not so good on slippery terrains like ice, water, and gravel, but they are better than RWD cars.
- The acceleration of an FWD car is inferior to a RWD car.
- The heavyweight (engine and transmission) at the front makes it difficult to handle at high speeds and heavy loads.
- It is tough to drive a FWD car on winding roads with sharp curves.
- Not good for towing trailers.
All-wheel drive (AWD) and 4-wheel drive (4WD) cars
Even though they are called by two different names (AWD and 4WD), both all-wheel drive and 4-wheel drive try to do the same thing. That is delivering the drive to all four wheels. However, they do it quite differently.
All-wheel drive (AWD) car
AWD cars normally have a longitudinally mounted engine at the front and the power flows to all four wheels. The construction of the drive train of an AWD car can differ from manufacturer to manufacturer.
But in a true AWD system, the power from the transmission flows first into the third or center differential. This ‘center differential’ takes care of the drive going into the differentials on the front and rear axles.
In a true all-wheel drive system, the four wheels of the vehicle are always connected to the drive system. And the drive goes to all four wheels at any given time.
AWD vehicles have a computer-like system placed in the transmission. This senses the requirement of traction at all four wheels and sends the power accordingly. In an AWD vehicle, the front and rear wheels can spin at different speeds.
However, in some low-end models of AWD cars, the drive may normally go to the front wheels. But when the situation demands (like slippage) the system can send the drive to the rear wheels.
These cars have a transfer case instead of the center differential. It can send the drive to the front wheels, rear wheels, or all four wheels as the situation demands.

Pros of an AWD car
- All four wheels are always linked to the drive system. Hence, the driver can drive it on a regular road or snow or wet road without worrying about the requirement of traction. Because the AWD system takes care of it. The system can send equal power to all four wheels or higher power to the front or rear wheels depending on the situation.
- AWD cars offer better handling capability on roads. They are good for occasional off-road driving. But 4WD cars are superior for off-road driving. AWD system is found on passenger cars that go occasionally off-road, wet patches, minivans, etc.
- AWD cars have good traction on slippery roads like ice, snow, and water
- Good acceleration.
- Good grip on the road when accelerating.
Cons of an AWD car
- All four wheels of an AWD car do not receive the same power all the time. This affects the performance of an AWD car on off-roads, hilly terrains, and crossing water.
- AWD vehicles are heavy, consume more fuel, and have less boot space and cabin space. This is when compared to an equivalent-size FWD car.
- AWD cars have a higher initial cost and high running and maintenance costs.
4-wheel-drive (4WD)
4WD cars normally have a longitudinally mounted engine at the front. As the name indicates, all four wheels receive the engine power. Most SUVs (Sports Utility Vehicles) come with a 4WD system since they give more traction and work well for off-road drives.
A 4-wheel drive car has a front differential, rear differential, and a fully locking transfer case. This is the major difference between an AWD and a 4WD system. A 4WD system has a fully locked transfer case. The driver of a 4WD car can disengage the front or rear wheels, but this is not possible in an AWD car.
The driver of a 4WD vehicle can select 4WD mode when driving off-road and shift to RWD/FWD when driving on normal roads. This arrangement improves fuel efficiency.
A 4WD car has a selectable low or high-gear range. This allows the driver to manually select low and high gear ranges. When there is a need to come out of tricky situations on rough terrain, you can switch over to low gear ratios that give higher torque at the wheels.
4WD system is normally found on off-road jeeps and light-duty trucks. Manufacturers designate them as 4 × 4, which means all four wheels receive the drive. You must select 4WD mode only when driving on wet or snowy roads or off-road. For driving on regular roads RWD/FWD mode should be used.

Pros of a 4WD car
- With a fully locked transfer case, the drive power is equally distributed to all four wheels. This makes a 4WD car excel on off-roads. 4WD cars are highly suitable for severe off-road driving like climbing hills, exploring canyons, crossing shallow water, driving over boulders, etc.
- 4WD cars are good for driving in slippery conditions like rain, snow, and ice.
- Most 4WD cars allow you to switch over to RWD/FWD when driving on regular roads.
Cons of a 4WD car
- You should never drive a 4WD car in 4WD mode on regular roads. Use two-wheel drive mode for roads. The downside is, that if you come across a slippery patch (snow or rain), you need to manually change the driving mode to 4-wheel drive.
- A 4WD car in 4-wheel mode does not perform well on normal roads. Because it needs to be driven in two-wheel drive mode on a normal road.
- 4WD cars normally have stiffer suspensions and the ride is not very comfortable.
- Increased weight and friction due to the added drive parts pull down its efficiency and fuel economy. This also increases vehicle cost and maintenance costs.
You may watch this video
Are AWD and 4WD drives are the same?
No! Even though the power from the engine reaches all four wheels in AWD and 4WD cars, there are key differences between the two drives.
- In a true all-wheel drive system, the four wheels of the vehicle are always connected to the drive system. And the drive goes to all four wheels at any given time. AWD vehicles have a computer-like system placed in the transmission. This senses the requirement of traction at all four wheels and sends the power accordingly. In an AWD vehicle, the front and rear wheels can spin at different speeds.
- A 4-wheel drive car has a front differential, rear differential, and a fully locking transfer case. This is the major difference between an AWD and a 4WD system. A 4WD system has a fully locked transfer case. The driver of a 4WD car can disengage the front or rear wheels, but this is not possible in an AWD car.
- The driver of a 4WD vehicle can select 4WD mode when driving off-road and shift to RWD/FWD when driving on normal roads.
- Even though both AWD and 4WD vehicles are used for off-road driving, a 4WD car excels itself as a super off-road vehicle. 4WD cars can cross any rough terrain including water, boulders, hilly areas, etc.
- A 4WD car allows to operate at low or high ratio ranges. The low ratio range gives maximum traction to climb on the boulders, cross rough off-road patches, water, and similar obstacles. And the high ratio range is good for slippery roads, rain, snow, or gravel. An AWD car does not have this feature.
- An AWD car is not as good as a 4WD car for an off-road drive, but it can cross a rough patch or overcome a sticky situation when required. An AWD car scores better on regular roads, compared to a 4WD car.
You may watch this video
Why the FWD cars are popular in India?
The reason for the popularity of FWD cars in India or elsewhere in the world includes the following:
- FWD cars give the best fuel efficiency. And highly suits the owners who mainly drive them for commuting between places in a city.
- FWD cars have maximum passenger space and luggage space, compared to other drive types.
- You can manage driving in slippery snow conditions by assembling a chain to the car tires.
- An FWD car has a low turning radius ideal for driving in a city.
- An FWD car has fewer transmission parts, a simpler design, and is easy to manufacture. This makes them cheaper to purchase and maintain than cars having other types of drives.
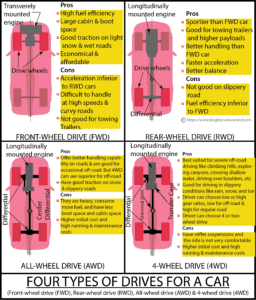
What is a differential and how does it work?
We will consider a rear-wheel drive vehicle to explain the working of a differential.
When a car turns a corner, it moves along a turning radius. One wheel at the inner arc and the other at the outer arc. The wheel at the outer arc should move faster than the wheel at the inner arc since it must cover more distance at the same time. This is made possible by a differential system of gearing.
You can define a differential as a device that can facilitate the two wheels on the same differential axle to run at different speeds. In a differential drive, the right and left wheels are mounted on two independent half-axles. These two half-axles are connected by the differential.
A differential receives the drive from the engine & transmission through the propeller shaft. It splits the drive between the two wheels and allows one wheel to run faster than the other while making a turn.
The differential unit is mounted on the rear axle and receives its drive from the engine through a propeller or drive shaft. The orientation of the propeller shaft is along the direction of car movement.
The differential unit receives the rotational movement from the propeller shaft and transmits it to the two half-axles. The two half-axles are positioned perpendicular to the propeller shaft and they drive the wheels.
The major parts of a differential are:
Drive pinion
The axis of the drive pinion is parallel to the direction of motion of the car and a drive/ propeller shaft connects this to the car’s transmission system.
Ring gear
The axis of the ring gear is in line with the axis of the axle on which the differential is mounted. The drive pinion meshes with the ring gear at 90⁰ and transmits the drive to it.
Side gears
There are two side gears one on the left axle and the other on the right axle. The mounting axis of the side gears is in line with the axle. The spider gears mesh with the side gear at 90⁰ and transmits the drive to it.
Spider gears
The number of spider gears can be from 1 to 4, depending on the vehicle. And the differential of a car may have 2 spider gears. The spider gears are mounted on the ring gear. When the ring gear rotates spider gears also rotate around the same axis.
Note: The ring gear is mounted on the differential casing, and spider gears are mounted on the ring gear.
Right and left axles with bearings and connected parts
The right and left axles rotate along with the side gear mounted on them and drive the wheels.
Working of a differential
The drive pinion transmits the power to the ring gear and makes it rotate. The two spider gears rotate along with the ring gear and around the same axis. But the spider gears can rotate on their own axis also.
The spider gears are connected to the left-side gear and right-side gear and transmit the drive to them and make them rotate.
When the car is on a straight path, the spider gears transmit equal speed to the left-side gear and right-side gear, and hence to the left and right wheels. And the spider gears do not turn on their own axis.
When the car is making a turn, due to the slippage, the spider gears rotate along with the ring gear and also on their own axis. This makes the outer wheel turn at a higher speed than the inner wheel. The car turns smoothly.
The above description is for an open differential and it has drawbacks when moving on slippery patches. To overcome the drawbacks, car manufacturers use ‘Limited Slip Differential.’
You may watch the video
Conclusion
Reading the preceding paragraphs of this article must have made you a bit wiser about the types of drives available in a car and the pros and cons of each drive system. But making your decision on a particular type of drive may still be confusing. The concluding paragraphs below may assist you.
- If the primary objective of driving the car is to meet your personal and work-related travel in a city or occasional outstation trips on normal roads, then an FWD car can be best for you. You can enjoy the advantage of fuel economy, large cabin space, boot space, and an easy-on purse. There are plenty of FWD cars of every brand to choose from.
- If you are a business owner and your work involves towing loaded trailers then you can go for an RWD car. An RWD car allows you to tow trailers, and carry loads, and it can cross a rough off-road patch occasionally.
- If you are into farming, live in the countryside, or drive on off-roads and roads affected by bad weather like snow and rain, an AWD or 4WD vehicle (Jeep or Pickup van) is good for you. Between AWD and 4WD, you can choose a 4WD Jeep if you are an ardent off-road driver and love to drive over rough hilly terrains, climb over boulders, and cross waters.
References