Introduction
The United States is the oldest democracy in the world, and India is the largest democracy. The major difference between the two democracies is that India has a parliamentary system of government, while the United States has a presidential system of government.
The heads of government of world democracies have different titles, but the most common titles are Prime Minister and President. The head of government in India is the Prime Minister and the head of government in the United States is the President.
This article discusses the differences between the election of the Prime Minister of India and the election of the President of the United States, as well as a few related topics.
How are they elected?
The Indian Prime Minister and the American President are elected indirectly, meaning they are not elected by the popular votes of their respective citizens.
India
The Election Commission of India (ECI) holds the parliamentary election for Lok Sabha to elect Members of Parliament (MP) for 543 parliamentary constituencies spread over the country.
After the parliamentary elections, the ECI constitutes the new Lok Sabha by notifying in the official gazette and publishing the list of 543 elected MPs with their affiliated political party. The ECI submits the certified list of the MPs in the new Lok Sabha to the President of India.
Each political party or coalition group holds a meeting of their respective elected MPs and elects their leader. The majority leader of the political party/group who enjoys the support and confidence of more than 50% of the MPs (273 or more MPS) meets the President and stake the claim to form the next government.
The president verifies the claim submitted by the majority leader of the Lok Sabha, appoints him/her as the Prime Minister-elect, and invites to form the government. The president can consult legal and constitutional experts before making a decision.
The Prime Minister and council of ministers take oath of office and the new government starts functioning.
Note: Normally the Prime Minister-elect is a member of the lower or upper house of parliament, if not, he/she must become a member of either house within six months.
United States
The election for the American President happens every four years on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in November.
The two major political parties in the United States are the Republican and Democratic parties. They hold state-level primaries, caucuses, and national-level conventions to democratically nominate their presidential candidates. There may be presidential candidates from small parties and their names appear on state-wise ballot based on fulfilling eligibility criteria.
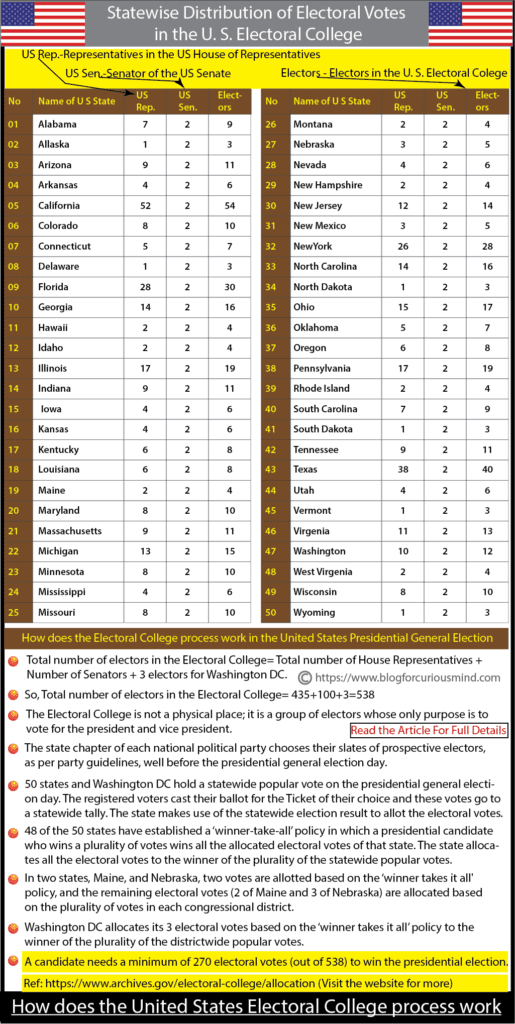
As per the United States Constitution, an Electoral College is formed to elect the President and Vice president. The Electoral College is a collection of electors and their job is to vote and elect the president-elect and vice president-elect. Each state has electors equal to their members in the Congress (House and Senate) and the federal district of Washington DC has 3 electors. The Electoral College has a strength of 538 electors.
The state chapters of both national political parties prepare their slate of electors for their state, and the presidential candidate of both national parties has their own state-wise slate of electors.
The laws relating to the Electoral College in 48 states and Washington DC state that the presidential candidate who wins the statewide plurality of popular votes will get all the electoral votes of that state. This is popularly known as the ‘winner-take-all’ policy. Two states, Maine, and Nebraska, allocate 2 electoral votes based on a ‘winner-take-all’ policy and the remaining based on the plurality of popular votes in each congressional district.
Based on the state-wise tally of the popular votes, the media publish the projected winner of the presidential election on election night.
The electors of the Electoral College of each state meet at their respective state capital on the first Tuesday after the second Wednesday of December and cast their votes for the President and Vice President. The electoral votes are sealed in a box and sent to the U.S. Congress.
The Senate and House of Representatives hold a joint meeting on the 6th of January to count and record the electoral votes received from 50 states and Washington DC. A presidential candidate must get a minimum of 270 electoral votes, out of 538, to become the president-elect.
The Congress certifies the electoral votes received from 50 states and Washington DC. The term of the new President begins on 20th January, the Presidential Inauguration Day.
Who finances the campaign?
India
The Indian political parties receive donations from individuals, corporates, and companies and use this for party expenses including elections.
The ECI has put a cap on the amount spent for campaigning by an individual contesting an election including for members of parliament to create a level playing field. The source of funds for a candidate can be his/her political party, own funds, and donations from the public and corporates. The ECI through its offices in each state monitors the expenditure made by each candidate.
United States
The presidential candidates in the United States raise campaign funds from individuals, corporates, and others. The candidates running for the president are required to register with the Federal Election Commission and follow the terms and conditions including appointment of Campaign Committees to manage the collection and spending of campaign funds.
Term period and number of terms in office
India
The Lok Sabha of the Indian parliament has a five-year term; hence the Prime Minister can have a maximum term of 5 years or until he/she enjoys the support and confidence of the majority Members of Parliament.
There is no limit on the number of terms for the Prime Minister of India. Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru was PM for more than 16 years, Smt. Indira Gandhi for more than 15 years, and the present PM Shri Narendra Modi has completed 10 years and is in his third term.
United States
The President of the United States has a four-year term in office and an individual cannot be elected as president for more than two terms.
Cabinet
India
The Prime Minister selects from the members of the Lok Sabha/Rajya Sabha of his/her political party for appointing members of his cabinet. If the appointed minister is not a member of parliament, then he/she should become a member of either house within six months.
United States
The President nominates his cabinet member and sends it to the Senate for approval. The cabinet members are experts in their fields and need not be members of Congress.
Government
India
The Prime Minister of India can lose the mandate when he/she loses the confidence of the supporting MPs. This leads to the resignation of the PM. The MPs may elect another leader to become the PM or it may lead to the dissolution of Lok Sabha and fresh elections.
United States
The President of the United States is not dependent on the strength of his/her party in Congress. The President will complete the four-year term unless he/she is impeached or incapacitated.
Voter registration
India
India has a centralized voter registration system and the Election Commission of India (ECI) manages the voter registration through the office of the State Election Offices. Every state has a State Election Officer subordinate to the ECI.
Indian citizens 18 years of age and older can register as voters. Local election offices hold special camps to encourage voter registration. There can be door-to-door visits by social and political party workers to mobilize voter registration.
United States
In the United States the state legislature is responsible for voter registration and to frame laws for the same. All citizens of the United States of 18 years of age and above are eligible to register for voting. However, apart from the age, the eligibility rules for voter registration can differ from state to state; for example, in some states, a convicted felon cannot vote.
Political parties
India
India has two main national-level political parties, Bhartiya Janata Party (BJP) and Indian National Congress (INC), but they do not have a strong presence in every Indian state. Many Indian states have strong regional political parties that have the state government under their control and the Members of Parliament of such political parties are normally aligned with and support one of the national political parties (BJP or INC).
United States
There are two main political parties in the United States, the Democratic Party and the Republican Party; there are states that predominantly support the Democratic Party and there are states that predominantly support Republican Party, and the remaining six or seven states are swing states that have a history of supporting one of the two main parties based on the presidential candidate and issues. Whichever candidate wins the swing states win with a very small margin. There are other parties like Green Party, Libertarian Party, and Independent Candidates but they are not capable of competing with the two main parties.
Selection of the candidate
India
In India, political parties can fight the Lok Sabha elections by pre-announcing their prime ministerial candidate or the winning members of parliament of the party can elect their leader after the election. India has seen both types of scenarios. Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, Smt. Indira Gandhi and the present Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi were the nominated prime ministerial candidates of their respective parties before the Lok Sabha election.
However, their nomination as the prime ministerial candidate was made by a group of top leaders of the party without involving all the members of their political party. Many Lok Sabha elections have resulted in a hung house and an unknown surprise candidate becoming the prime minister.
United States
The major political parties of the United States, the Republican and Democratic parties conduct state-level primaries and caucuses in each state and the candidates of each party fighting for their party’s nomination, campaign to win the delegates of each state. Each state allocates the delegates to the contesting candidates based on voting and the voting is open to members of the political party. The national convention of the respective political party considers the delegates won by each candidate and whoever wins maximum delegates is nominated as their presidential candidate.
Voting process
India
The Election Commission of India conducts the Lok Sabha elections in multiple phases that enable it to deploy sufficient para-military forces for conducting peaceful election and to ensure even the remotest voter is facilitated to vote. People visit their assigned polling booths on the voting day and cast their vote on EVM (Electronic Voting Machine). Normally, the polling booths are within walkable distances.
United States
In the United States, the voting for the Presidential General Election is typically conducted throughout the country on a predetermined date, on the first Tuesday after the first Monday of November in the election year. The states have the responsibility of managing the elections and hence the ballot can contain other races also.
The registered voters visit the polling stations to cast their votes. Depending on the state the voter may have the choice of voting through mail-in ballot or early voting.
Legislative body
India
The parliament of India is bicameral, meaning it has two houses and a president. The lower house is Lok Sabha whose members are directly elected by the people, and the upper house Rajya Sabha (also called Council of States) whose members are elected by the state legislative assemblies.
The members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha are called Members of Parliament of their respective houses. The present strength of the Lok Sabha is 543 and Rajya Sabha is 250 (including 12 nominated members).
United States
The legislature of the United States is the U.S. Congress. The House of Representatives and the Senate are the two chambers of Congress.
The members of the House of Representatives represent the congressional districts of their respective states. The present strength of the House of Representatives is 435. The number of House Representatives allocated to each state is based on the state population and is subject to change after each census.
The members of the Senate represent their respective states. Each state has two senators and the total number of senators is 100 (50 states × 2).
You may like to read the following articles:
Who elects the prime minister of India?
Who elects the President of the United States