Introduction
A boat and a ship float on water, and a stone sinks in water, but a submarine is capable of floating, sinking to the desired depth, moving underwater, and rising again to the surface of the water. Submarines are capable of diving underwater up to a depth of 800 feet or more. Do you know how a submarine does this?
Well, there is no magic in this, and it happens only by proper application of the principles of science.
Do you want to know the science behind how a submarine sinks and floats on water? Please continue to read this article.
How does a submarine sink and float on water?
We all know that any object, partially or fully immersed in a fluid experiences an upward thrust (force) called buoyancy or buoyant force. Archimedes principle, put forth by the great Greek Mathematician Archimedes states that any object partially or fully immersed in a fluid (like water) experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
The weight of the object acts downwards and the buoyant force acts upwards. Whether an object floats or sinks depends on its buoyancy. The object floats if the buoyant force (equal to the weight of the fluid displaced) is more than or equal to the weight of the object and the object sinks if the weight of the object is more than the buoyant force.
Suppose, an object constructed to float on water has a mechanism to increase and decrease its weight, then the crew controlling it can make the object float, sink to a particular depth, and rise again to the surface; this can be done by manipulating the weight of the object. This is the technic behind how a submarine floats, sinks, and rises again. Let us understand this in detail.
A submarine has ballast tanks with air vents at the top and valves at the bottom. A submarine uses its ballast tanks to vary and control its buoyancy in water or we can say the buoyancy of a submarine is controlled by its ballast tanks.
When the submarine is floating on the surface, the ballast tanks are filled with compressed air, and the vents and valves are closed. In this situation, the weight of the water displaced by the submarine (buoyant force) is equal to or more than the weight of the submarine, so the submarine floats.
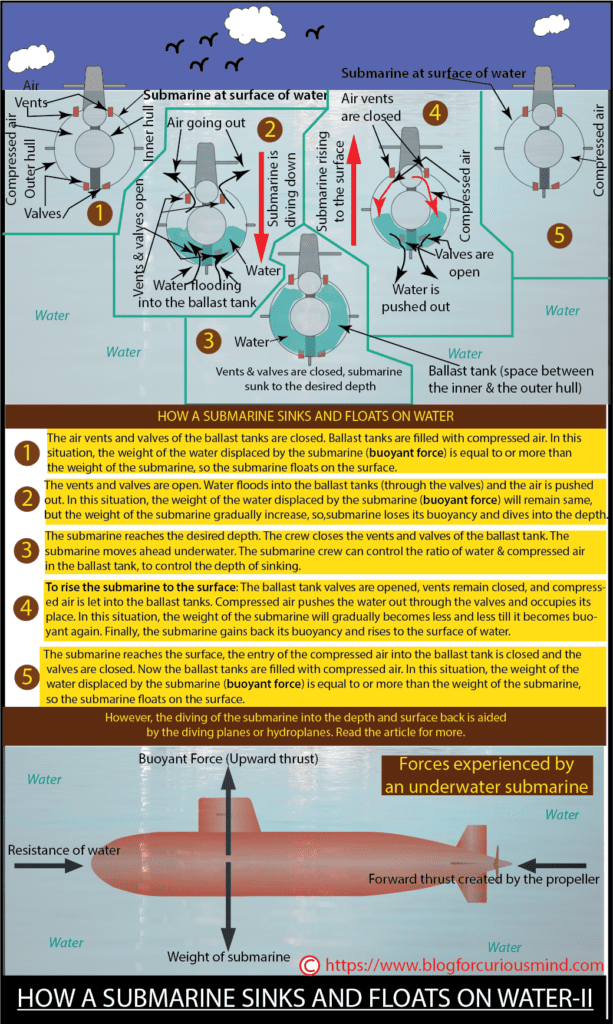
To sink the submarine into the depth of water, the air vents at the top and the valves at the bottom of the ballast tanks are opened. Water floods into the ballast tanks pushing the air out, and the air goes out through the vents. As the ballast tanks are filled with water, the submarine loses its buoyancy and sinks. In this situation, the weight of water displaced by the submarine (buoyant force) remains the same, but there is an increase in the weight of the submarine, due to the presence of water in ballast tanks. So, the submarine sinks to the desired depth and moves ahead underwater. The crew manning the submarine can control the ratio of air and water in the ballast tanks.
When the crew wants the submarine to rise to the surface, the air vents remain closed, valves are opened, and the compressed air is let into the ballast tanks. The compressed air pushes the water out through the bottom valves and occupies the place of water. This increases the buoyancy of the submarine and it rises to the surface. In this situation, the weight of water displaced by the submarine (buoyant force) is more than or equal to the weight of the submarine. So, the submarine is buoyant again, rises to the surface and floats.
However, the diving down of the submarine into the depth of water and resurfacing again is not as simple as explained above, and most submarines do not dive into the depth and resurface vertically. A submarine has diving planes (or hydroplanes) and this plays an important role when the submarine dives into the water and rises back to the surface.
There are two pairs of diving planes (or hydroplanes), one fitted at the at the bow (front) of the submarine and another at the stern (rear). Many submarines have sailplanes (located on the sail) instead of bow planes. Diving planes help the submarine to pitch its bow down and stern up to aid the process of submerging and pitch its bow up and stern down during rising. They also help in monitoring the depth when the submarine remains underwater.
So, we can summarise that a submarine floats on water when it has positive buoyancy and the ballast tanks are filled with air. And it dives down when it has negative buoyancy and the ballast tanks are filled with water. The depth of the submarine underwater can be controlled by controlling the ratio of water and air in the ballast tanks. The diving planes or hydroplanes assist the submarine in diving into the water and rising back to the surface.
You can view this and this YouTube videos.
A small brief about submarine

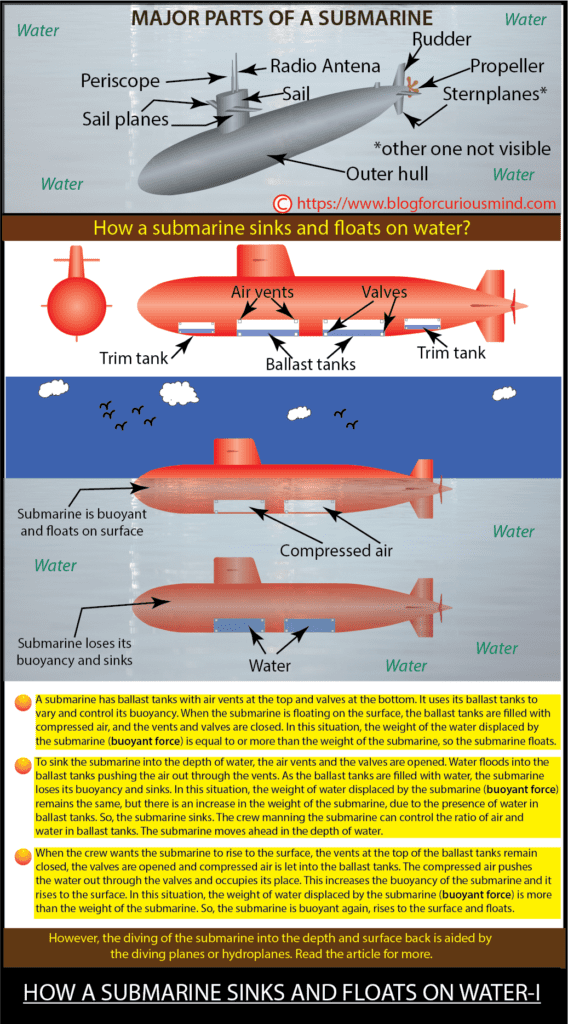
A submarine is a cylindrical closed vessel and has two hulls, an inner hull, and an outer hull. The inner hull (called pressure hull) houses the crew and machinery and it is built to protect the crew from the enormous water pressure and freezing temperature of the ocean depth. The outer cylindrical-shaped hull is the submarine’s body. The ballast tanks and trim tanks are located in between the inner and outer hulls.
The major parts of a submarine are (i) the Inner and outer hull (ii) the sail (iii) the sailplanes (iv) the rudder (v) the stern planes (vi) the propeller (vii) the periscope (viii) ballast tanks (ix) trim tanks and (x) radio antenna.
An underwater submarine experiences the following forces:
- Buoyant force (upward thrust)
- Weight of the submarine (acting downwards)
- Resistance offered by water for the moving ahead of the submarine
- Forward thrust, generated by the rotating propeller.
Both ships and submarines have ballast tanks, but they use it differently. A large boat and ship use its ballast tank for achieving hydrostatic stability, but a submarine uses its ballast tanks primarily to vary or control its buoyancy. Trim tanks are used to maintain the correct level.
View this and this YouTube videos for more on submarine.
Conclusion
In the preceding paragraphs, we had a detailed discussion on how a submarine sinks and floats on water and the science behind it. We hope this article was able to give some input to you.
You may read the following articles
Parts of a boat and anatomy of a boat
Caution
The only purpose of this article is to share information. The author makes no claims regarding the accuracy or completeness of the content of this article. The intention of this article is to share information and it is not a guide for aspiring sailors. If you are interested in learning sailing, please enroll yourself in a government-approved Boating Academy or Institute near you.
Please read similar articles How a ship floats on water? And Parts of a boat and anatomy of a boat.
References https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diving_plane#:~:text=Diving%20planes%20are%20usually%20fitted,they%20introduce%20a%20pitching%20moment.

